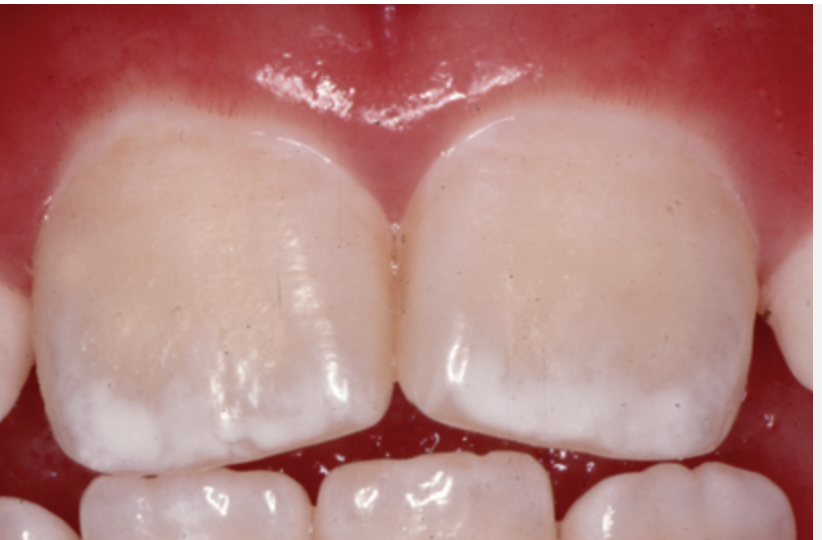
Fluorosis in children
Fluorosis is a cosmetic condition that can affect children who consume too much fluoride during the development of their teeth. It is caused by an overexposure to fluoride during the time when the teeth are forming, which can lead to changes in the appearance and texture of the tooth enamel.
Mild fluorosis can cause small white spots or streaks on the teeth, while more severe fluorosis can cause brown or black stains and pitting or mottling of the enamel. Fluorosis does not typically affect the function or health of the teeth, but it can be a cosmetic concern for some individuals. Fluorosis can occur when children consume too much fluoride from multiple sources, such as fluoride supplements, fluoridated water, and fluoride-containing dental products. It is important for parents to monitor their child's fluoride intake and to follow the recommendations of their dentist or pediatrician regarding fluoride supplementation.
Prevention of fluorosis includes monitoring the child's fluoride intake, using appropriate fluoride-containing dental products, and supervising children's brushing habits to ensure that they do not swallow toothpaste or mouthwash. If a child shows signs of fluorosis, their dentist may recommend cosmetic treatments such as tooth whitening or dental bonding to improve the appearance of the affected teeth.
Overall, fluorosis is a cosmetic concern that can be prevented by monitoring a child's fluoride intake and following the recommendations of dental professionals. If you have concerns about your child's fluoride intake or the appearance of their teeth, it is important to consult with a dentist or pediatrician.